Hydrogenation .
200 INR/Kilograms
Product Details:
- Product Type Hydro genation
- Storage Room Temperature
- Application Pharmaceutical
- Purity High
- Click to View more
X
Hydrogenation . Price And Quantity
- 200 INR/Kilograms
- 25 Kilograms
Hydrogenation . Product Specifications
- High
- Hydro genation
- Pharmaceutical
- Room Temperature
Hydrogenation . Trade Information
- 5000 Kilograms Per Month
- 7 Days
- All India
Product Description
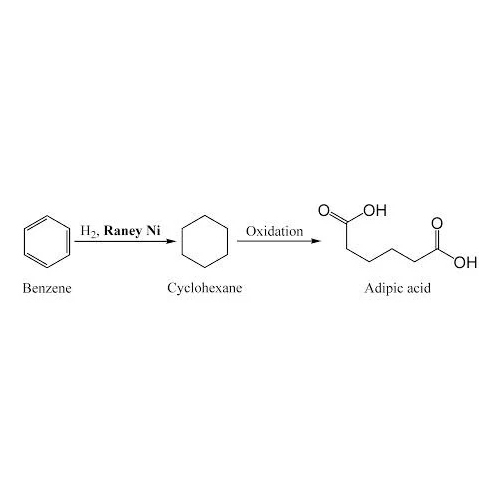
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction in which hydrogen H2 is added to another compound typically an unsaturated organic compound resulting in the saturation of carboncarbon double or triple bonds This process can occur under various conditions and with different catalysts depending on the specific reaction requirements and desired products Heres a comprehensive overview of hydrogenation
Types of Hydrogenation
1 Catalytic Hydrogenation
Process Catalytic hydrogenation is the most common method involving the use of a catalyst to facilitate the addition of hydrogen to unsaturated compounds
Catalysts Common catalysts include metals such as nickel Ni palladium Pd platinum Pt and ruthenium Ru often supported on a substrate like carbon or alumina
Conditions Typically carried out under elevated temperature and pressure to enhance reaction rates and efficiency
2 Selective Hydrogenation
Purpose Selective hydrogenation allows for the partial saturation of specific bonds while leaving others intact
Applications It is crucial in industries like food processing eg edible oils and fine chemicals where maintaining certain functional groups or preventing overhydrogenation is necessary
3 Asymmetric Hydrogenation
Chirality In asymmetric hydrogenation the catalyst used induces chirality handedness in the resulting molecule producing enantiomerically pure compounds
Applications Its essential in pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries for producing chiral intermediates and active ingredients
4 Photochemical Hydrogenation
Light Activation This method uses light energy often ultraviolet or visible light to activate hydrogen atoms enabling them to react with unsaturated compounds under milder conditions compared to thermal catalytic hydrogenation
Applications of Hydrogenation
1 Food Industry
Edible Oils Hydrogenation is used to convert liquid vegetable oils into solid or semisolid fats hydrogenated fats improving texture shelf life and heat stability for food products like margarine and shortening
Flavor and Fragrance It is employed in the synthesis of aroma compounds and flavoring agents
2 Chemical Industry
Fine Chemicals Hydrogenation plays a vital role in synthesizing pharmaceuticals agrochemicals and specialty chemicals by modifying functional groups and improving chemical stability
Polymers It can be used to modify the properties of polymers by altering their molecular structure and properties
3 Petroleum Refining
Fuel Production Hydrogenation processes are employed in refining crude oil to produce cleanerburning fuels and to remove sulfur compounds desulfurization
4 Environmental Applications
Environmental Remediation Hydrogenation can be used in environmental cleanup processes to degrade hazardous compounds such as chlorinated solvents into less harmful substances
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Safety Hydrogenation reactions involving high pressures and reactive catalysts require careful handling to ensure safety
Environmental Impact Concerns include energy consumption and potential waste generation associated with catalysts and reaction byproducts Efforts are made to develop greener catalytic systems and optimize processes for minimal environmental impact
Conclusion
Hydrogenation is a versatile chemical process with applications spanning various industries from food production to pharmaceutical manufacturing and environmental remediation Understanding the principles and applications of hydrogenation is crucial for optimizing processes improving product quality and addressing environmental considerations
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email



 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS
